Rodent Control Program
1.Rodent Facts

1.1.Because rodents often live and hang out in garbage dumps, sewers, and other unsanitary places, they spread bacteria and diseases such as salmonella, E. coli, and dysentery. Source
If you can fit a pencil into a gap or hole, a mouse can fit through a 1/4-inch diameter hole!
1.2.Ever wonder why rodents gnaw? Because their incisors never stop growing, they need to chew and gnaw to prevent their teeth from growing into their skulls.
1.3.In 6 months, a pair of mice can eat 1.80 kg (4 lbs) of food, and their urine and feces can contaminate 10 times that amount of food. Likewise, the feces they produce in 6 months can contaminate packaging and surfaces that come into contact with food.
2. Methods of rat control
Environmental management, chemical agents and physical control are adopted to control rat infestation.
2.1. Environmental management: Comprehensively and continuously remove indoor and outdoor debris, garbage and dirty corners, manage the internal and external environment, and eliminate rat habitats
Ⅰ Sewers, drains and various pipes leading to the room should use one-way valves or add rat-proof nets and rat-blocking boards
Ⅱ The windows and all vents in the basement and the first floor should be equipped with wire mesh, and the mesh should be less than 13X13mm.
Ⅲ Doors and windows should be closed, with a gap less than 6mm, and iron sheets should be inlaid under the doors.
Ⅳ All holes (pipeline wells) for pipes and cables entering and exiting buildings should be blocked with cement.
Ⅴ All holes and gaps in the building should be smoothed with cement to prevent rats from hiding and using them.
2. 2. Chemical control
(1) Rodenticide is 0.005% brodifacoum corn bait (or brodifacoum bait).
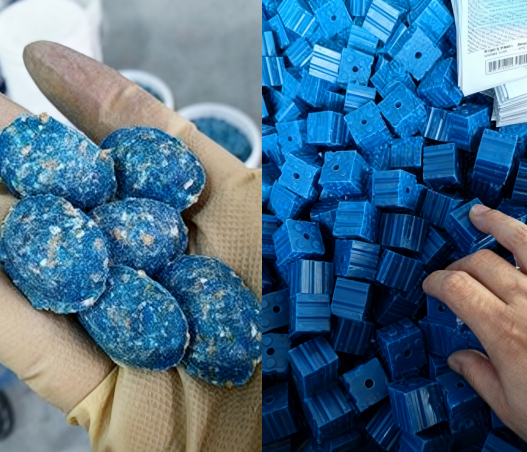

(2) For above-ground areas (indoor and outdoor environments), use the saturated baiting method. Place one pile of 20-30 grams per 15 square meters indoors. Rat poison is placed in indoor kitchens, warehouses, storehouses and other places where rodents are present. In residential areas, it is placed in hidden places and should be placed as much as possible. A bait station should be set up along the long line of 30-50 meters along the wall.
(3) Waterproof and moisture-proof wax block bait is placed in underground areas of cities and towns (various trenches).
(4) Rat poison must be placed in indoor bait boxes and outdoor bait stations. The coverage rate, arrival rate, saturation rate and retention rate of rat poison placement should all reach more than 90%. On the 2nd to 5th day after the application of the drug, 2-3 inspections should be carried out to check for omissions and fill in the gaps. The principle should be to observe frequently and replenish as much as possible. If more than 1/4 of the baiting points are completely eaten up, it means that there are too few baiting points and more baiting points should be added.
(5) Killing free rodent parasites: In order to prevent free rodent parasites from biting people and causing disease transmission after rodent control, a residual spray of sanitary insecticide should be carried out in the indoor environment if conditions permit while rodent control.
2.3. Physical control:
Where rat poison cannot be used to kill rats, mouse traps, mouse cages, and sticky mouse boards can be placed in places where rats often appear.
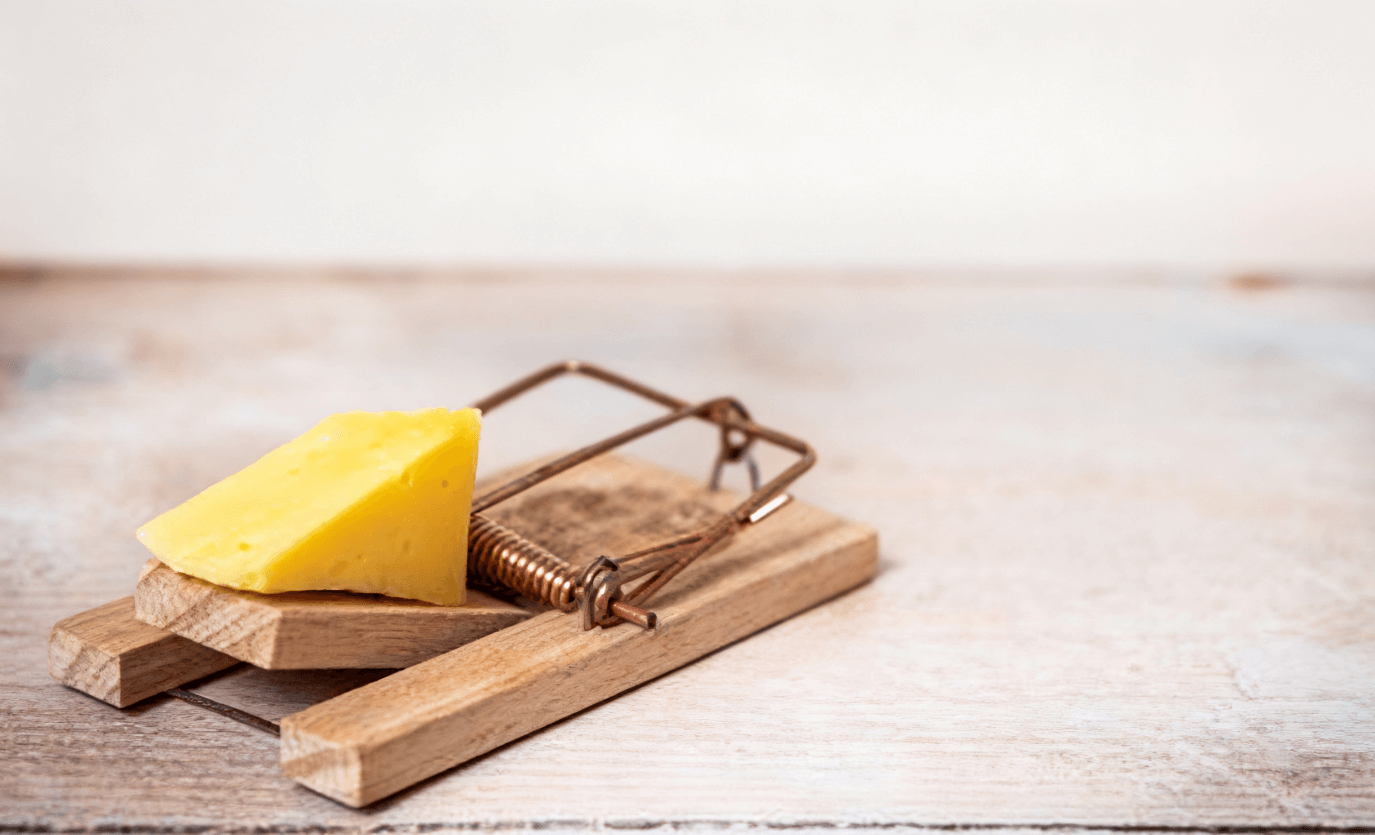
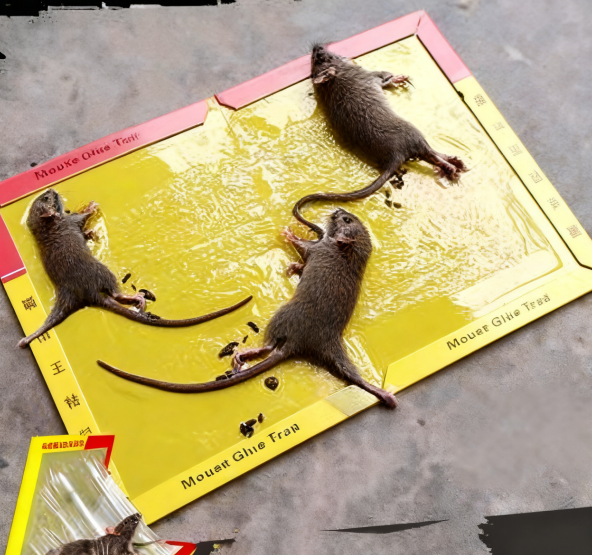
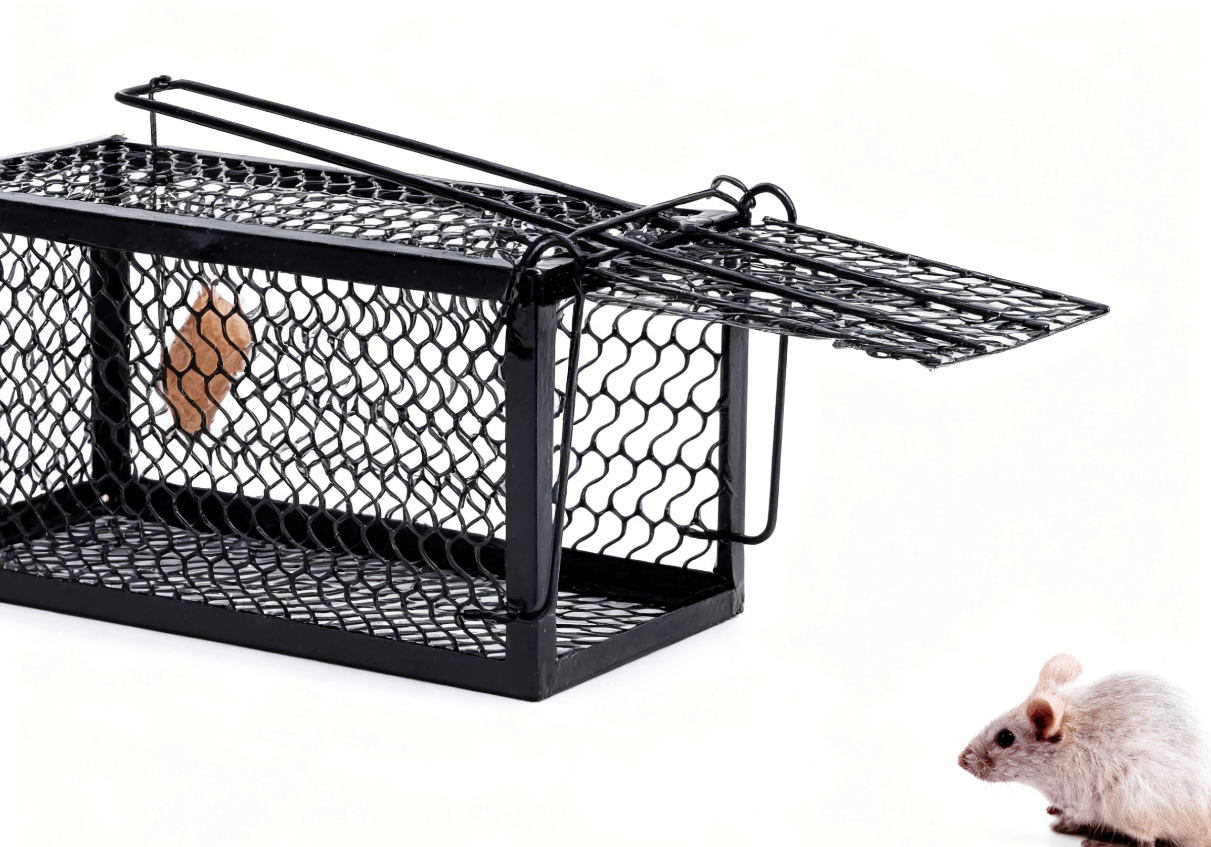


After using drugs to kill rats, mouse traps and mouse cages should be replaced at intervals for killing rats, which can be done all year round. The structure of the trap cage needs to be kept sensitive, the bait should be replaced in time, and the tools used to catch rats need to be cleaned. Usually, they can be used alternately every month to consolidate the effect of killing rats.
3. Rat control standards
(1) Powder method: Place two 20×20 cm talcum powder blocks in a standard room of 15 square meters. After one night, the number of positive powder blocks shall not exceed 3%.
(2) Visual inspection method: The number of rooms with traces of rat holes, rat feces, rat bites, etc. shall not exceed 2%.
(3) Night trap method: The rat density shall not exceed 1%
The failure rate of rat control facilities in key units shall not exceed 5%.
Other information


