Keep these herbicide damage remedies in mind
There is an old Chinese saying that goes, "If you don't hoe the ground in summer, you will go hungry in winter." This means that if you don't weed and loosen the soil in summer, the harvest will be poor and you will go hungry in winter. Since weeds grow fast and vigorously in summer, they easily compete with crops for fertilizer, light, and water, affecting the normal growth of crops. Therefore, weeding in summer can reduce the damage caused by weeds and pests, and achieve the effect of increasing production and improving quality. The following common problems in the use of herbicides and methods for identifying and mitigating herbicides are for your reference.

1.Problems that may occur during the use of herbicides
1.1. Main manifestations: failure to kill weeds, crop damage
1.2. Reasons for failure to kill weeds
(1)Quality of the herbicide: poor emulsification and dispersibility, sedimentation and agglomeration; insufficient dosage: low registered dosage;
(2)high weed density; inability to penetrate the herbicide; increased weed resistance, long-term single use of herbicides, causing weeds to produce resistance genes, which are dominant genes, and resistance genes are rapidly transmitted through pollen drift;
(3)technical problems in the application of pesticides, sprayer failure, uneven spraying, missed spraying, etc.; straw and wheat stubble blocking, the weeds below cannot contact the liquid medicine.
1.3. Reasons for the occurrence of pesticide damage
Wrong pesticide, nicosulfuron was applied to peanuts; wrong dosage, 3 acres of pesticide was sprayed on 1 acre; climate reasons: stem and leaf herbicides encountered high temperature and drought; soil treatment agents encountered heavy rains, and water was stored in the field; crop varieties: glutinous corn and sweet corn are sensitive to nicosulfuron.
4. How to avoid the above problems
Select the right medicine (according to the crop and the grass phase); use the medicine accurately (low dosage for young grass and low density, high dosage for old grass and high density); spray the medicine evenly (use water volume and spray well); use the medicine at the right time (no wind, before 10 am, after 4 pm, 3-5 leaf stage).
2.Phytotoxicity is a common problem encountered in the use of herbicides, and it is also the most concerned issue.
Main manifestations: growth inhibition, yellowing and withering of heart leaves, leaf dryness and leaf fall, deformed root of plant leaves, leaf bleaching, and plant withering.
2.1Symptoms of phytotoxicity of main categories of herbicides
(1)Sulfonylurea herbicide phytotoxicity
Manifestation: yellowing of leaves, growth inhibition
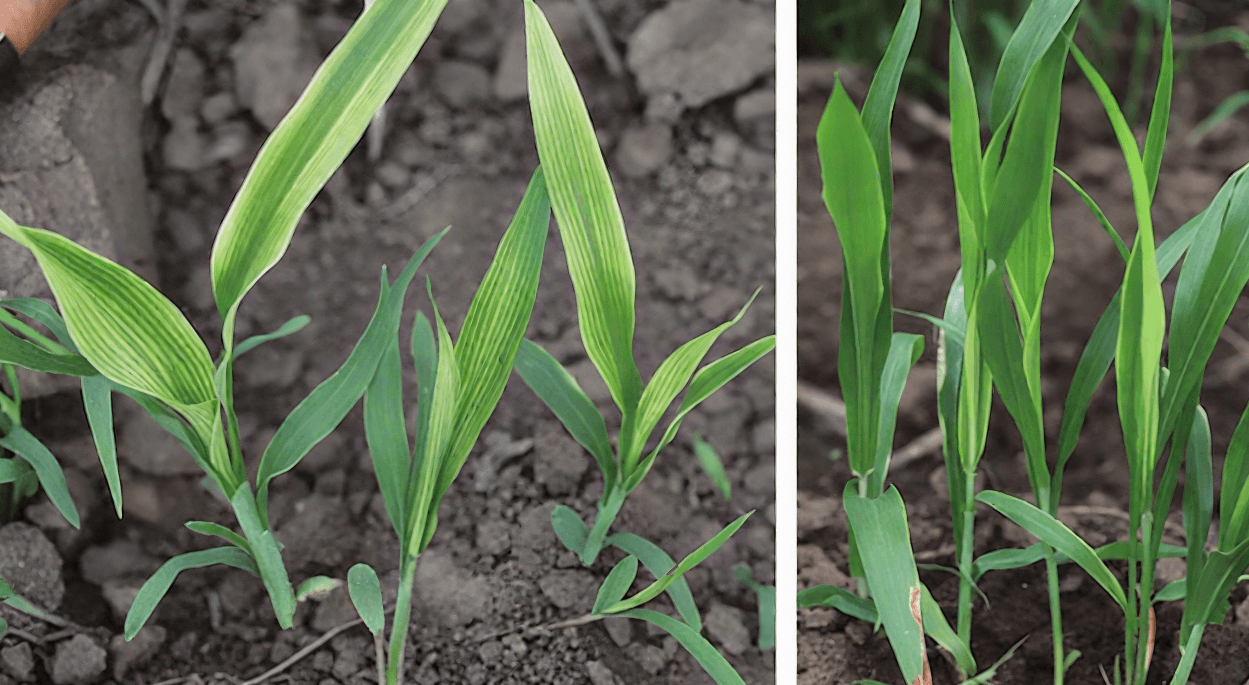

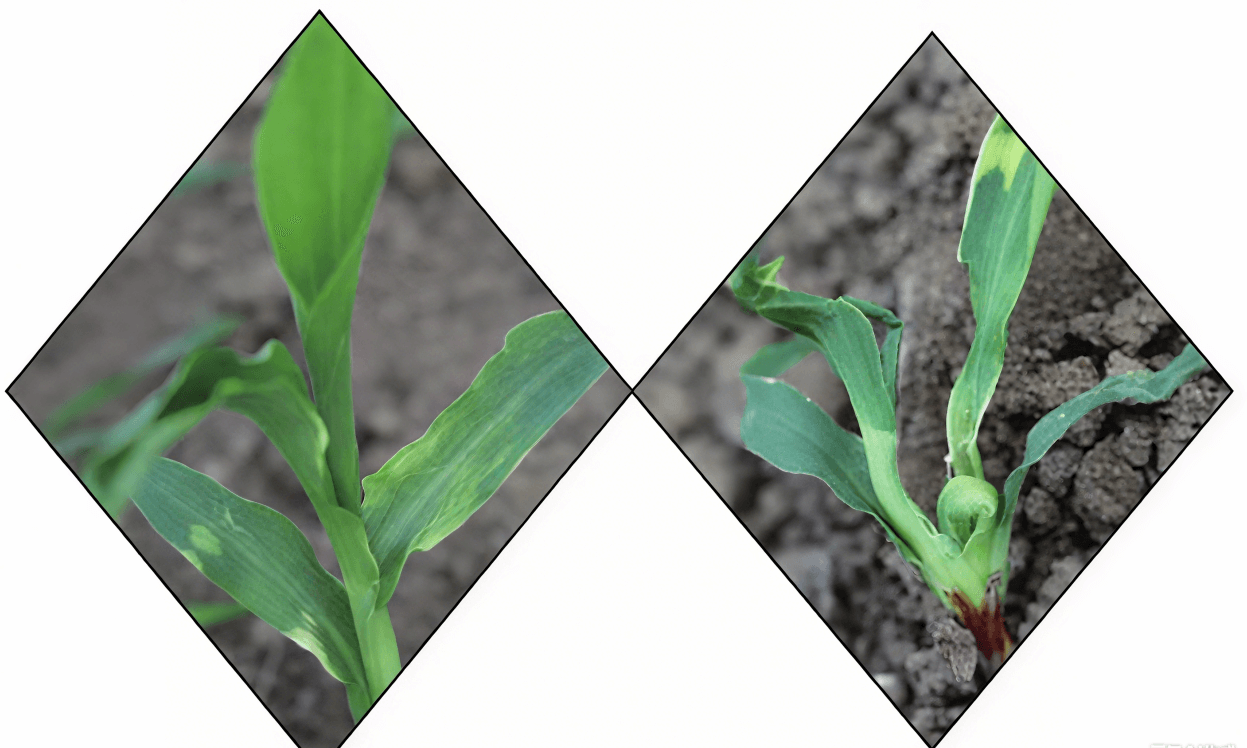
(2)Hormone herbicide phytotoxicity
Manifestation: deformed, onion-like leaves
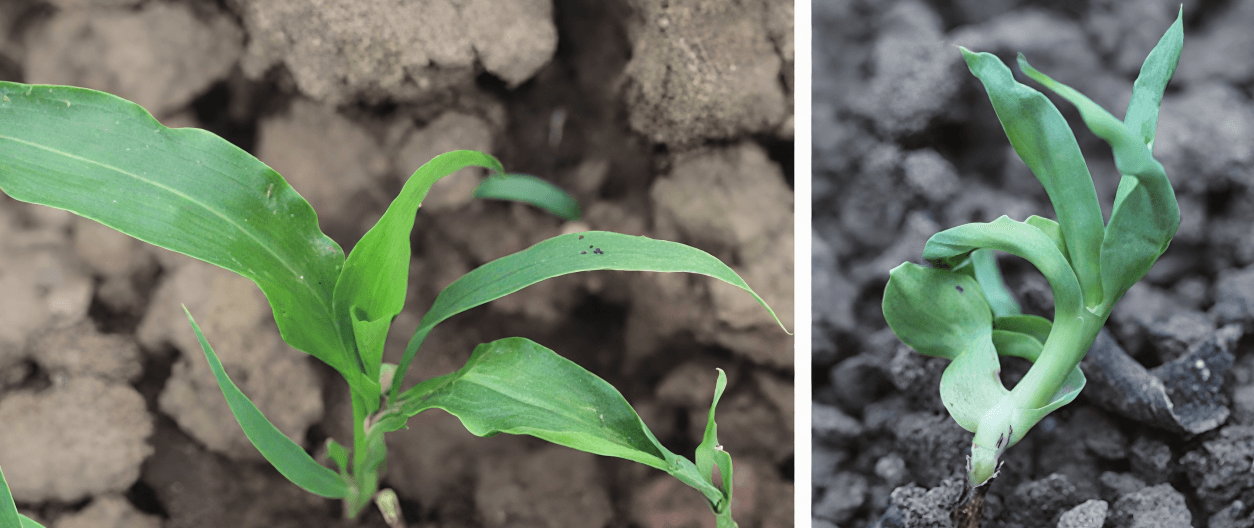

(3) Amide herbicide phytotoxicity
Manifestation: affecting germination, slow growth, turning green and brittle
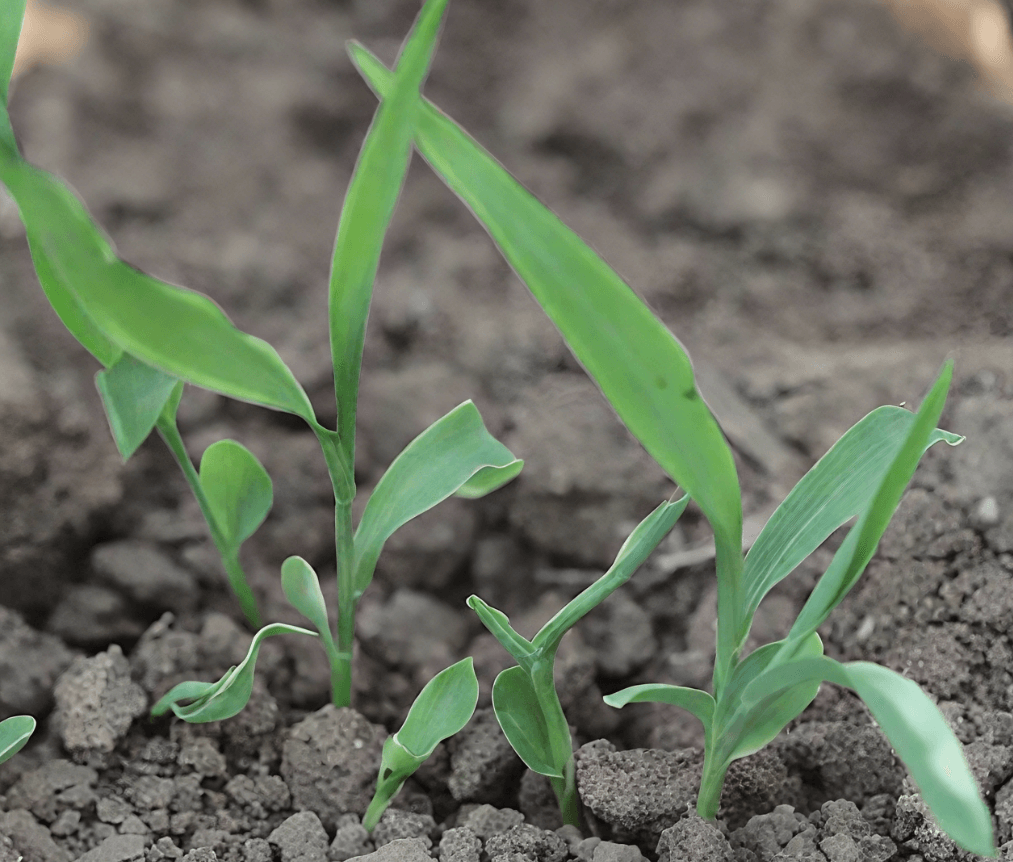

(4) Triazine herbicide phytotoxicity
Manifestation: growth inhibition, yellowing of leaves, and dwarf plants
(5) Bipyridine herbicide phytotoxicity
Manifestation: yellow spots on leaves

(6) Triketone herbicide phytotoxicity
Manifestatio
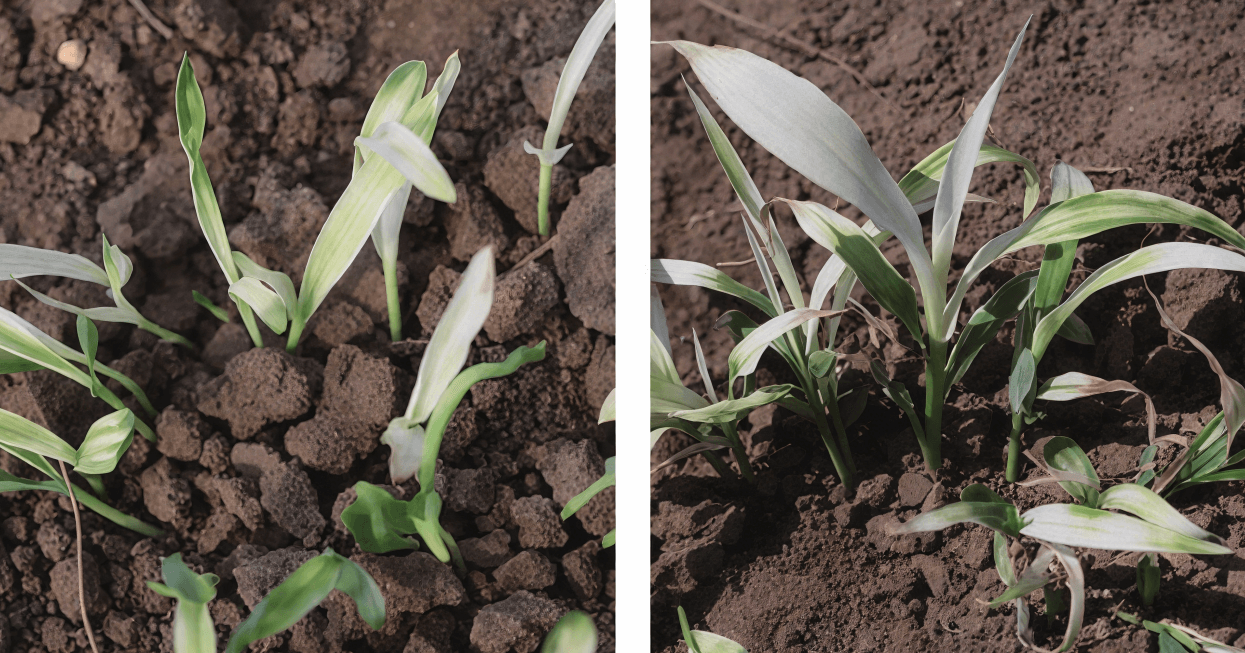

n: whitening of leaves
3.Measures to alleviate pesticide damage
3.1. Strengthen fertilizer and water management, apply quick-acting fertilizer and water. Promote early seedling growth and enhance corn resistance.
3.2. Apply micro-fertilizers and plant growth regulators to promote growth.
3.3. Apply herbicide antidotes.
Common antidotes include: NA, dichlormid, benoxacor, fenchlorazole, fenclofim, mefenpyr-diethyl, flurazole, Cloquintocet-mexyl, BAS145138



